BUY vs REPAIR - SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES

REASONS TO BUY OR REPAIR SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
WHEN TO BUY OR REPAIR SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
WHY TO BUY OR REPAIR SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
Special steam turbines are typically designed for specific applications and are often critical to the operation of the plant. The decision to buy or repair special steam turbines should be based on a number of factors, including the age and condition of the equipment, the cost of repair versus replacement, and the impact on the plant’s operations.
Here are some reasons and actions to consider:
Reasons to buy a special steam turbine:
Improved efficiency: Newer steam turbines are generally more efficient than older models, which can lead to energy savings and cost reductions.
Increased reliability: Newer steam turbines are typically more reliable than older models, which can help reduce unscheduled shutdowns and maintenance costs.
Advanced features: Newer steam turbines often come with advanced features such as condition monitoring, which can help identify potential issues before they become major problems.
Actions to take when buying a special steam turbine:
Conduct a thorough evaluation: Before purchasing a new steam turbine, it’s important to conduct a thorough evaluation of the plant’s needs and the available options. This may include an analysis of the plant’s energy requirements, as well as a comparison of different steam turbine models.
Consider the cost: The cost of a new steam turbine can be significant, so it’s important to weigh the benefits against the cost of repair and maintenance for the existing equipment.
Choose a reputable supplier: When purchasing a new steam turbine, it’s important to choose a reputable supplier with a proven track record of delivering high-quality equipment and providing excellent customer support.
Reasons to repair a special steam turbine:
Cost-effective: In some cases, repairing a special steam turbine may be more cost-effective than purchasing a new one.
Limited downtime: Repairing a steam turbine can often be completed more quickly than purchasing and installing a new one, which can help reduce downtime and maintain plant operations.
Preserve existing equipment: If the steam turbine is a critical part of the plant’s infrastructure, repairing it may be the best option for preserving existing equipment.
Actions to take when repairing a special steam turbine:
Conduct a thorough evaluation: Before repairing a steam turbine, it’s important to conduct a thorough evaluation of the equipment to determine the root cause of the issue and the extent of the repairs required.
Choose a reputable service provider: When selecting a service provider to repair the steam turbine, it’s important to choose a reputable company with a proven track record of providing high-quality service.
Plan for downtime: Repairing a steam turbine will require some amount of downtime, so it’s important to plan accordingly and ensure that any necessary maintenance is performed during this time to avoid future issues.
The decision to buy or repair a special steam turbine depends on several factors, including the age and condition of the turbine, the required level of reliability and performance, the availability of spare parts and maintenance resources, and the overall cost-effectiveness of the options. Here are some reasons and actions to consider:
When to buy:
Obsolescence: When a special steam turbine is outdated and no longer supported by the manufacturer, it may be more cost-effective to buy a new one that meets the latest standards and technology.
Capacity expansion: When there is a need for increased power output or additional operational capacity, buying a new steam turbine may be a better option than trying to modify or upgrade an existing one.
Economic considerations: If the cost of repairing a steam turbine exceeds a certain threshold, it may be more cost-effective to buy a new one, especially if the new turbine is more efficient and has lower operating costs.
Actions when buying:
Conduct a thorough analysis of the plant’s power requirements, including load profiles and operating conditions, to determine the appropriate size and capacity of the new turbine.
Evaluate the latest technology and design options to ensure that the new turbine is reliable, efficient, and easy to maintain.
Work closely with the manufacturer and suppliers to ensure that the new turbine is properly installed, commissioned, and integrated into the existing power plant.
When to repair:
Age: If the special steam turbine is relatively young and still has many years of useful life left, repairing it may be a better option than replacing it with a new one.
Maintenance history: If the turbine has been well-maintained and has a good track record of reliability and performance, repairing it may be a more cost-effective option than buying a new one.
Availability of spare parts: If the necessary spare parts are readily available and the repair costs are reasonable, it may be more practical to repair the steam turbine rather than buying a new one.
Actions when repairing:
Conduct a thorough inspection and analysis of the turbine to identify the root cause of the problem and determine the extent of the repair required.
Use genuine spare parts and follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance procedures to ensure that the turbine is restored to its original condition.
Perform regular preventive maintenance to ensure that the turbine remains in good working order and to avoid unscheduled shutdowns.
Here are some recommendations and actions for whether to buy or repair special steam turbines:
Evaluate the age of the turbine: If the turbine is relatively new and has not experienced significant wear and tear, then it may be more cost-effective to repair the turbine rather than buying a new one. On the other hand, if the turbine is approaching the end of its useful life, it may be better to invest in a new turbine to avoid the risk of critical failures and unscheduled shutdowns.
Assess the condition of the turbine: Conduct regular inspections and maintenance checks to determine the condition of the turbine. If the damage is minimal and can be repaired easily, then repair may be the best option. However, if the damage is extensive or if the turbine is in poor condition, then buying a new turbine may be necessary to ensure reliability, availability, and safety.
Consider the cost: Compare the cost of repairing the turbine to the cost of buying a new one. If the cost of repair is significantly lower than the cost of a new turbine, then repairing may be the more economical choice. However, if the cost of repair is close to or exceeds the cost of a new turbine, then buying a new turbine may be the better option in terms of long-term cost-effectiveness.
Determine the availability of spare parts: If spare parts for the turbine are readily available, then repairing the turbine may be a viable option. However, if spare parts are scarce or difficult to obtain, it may be more practical to buy a new turbine that has readily available spare parts.
Consult with experts: Consult with turbine experts, manufacturers, and maintenance specialists to get their recommendations and advice on whether to buy or repair the turbine. These experts can provide valuable insights into the condition of the turbine and the best course of action to ensure reliability, availability, maintainability, and safety.
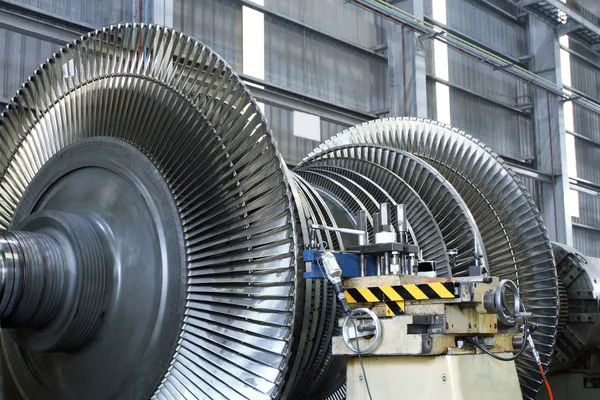

WHAT TO BUY OR REPAIR IN SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
HOW TO BUY OR REPAIR IN SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
WHO MUST BUY OR REPAIR SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
The decision to buy or repair a special steam turbine depends on the specific circumstances of the plant and the turbine itself. Here are some general recommendations and actions to consider:
Assess the condition of the turbine: Before deciding to repair or replace a special steam turbine, it is important to assess its current condition. This can be done through inspections, testing, and analysis of operational data. This will help determine the extent of repairs needed and whether replacement is a better option.
Evaluate the cost: Repairing a special steam turbine may be less expensive than purchasing a new one, but it’s important to consider the long-term cost of maintenance and potential downtime. On the other hand, purchasing a new turbine can be expensive, but it may offer more advanced technology and improved efficiency.
Consider the age of the turbine: Age is an important factor to consider when deciding whether to repair or replace a special steam turbine. If the turbine is approaching the end of its expected lifespan, it may be more cost-effective to replace it rather than continue to repair it.
Evaluate the availability of spare parts: If the special steam turbine is an older model or has been customized for the plant, spare parts may not be readily available. This can lead to extended downtime if repairs are needed. In this case, purchasing a new turbine with readily available spare parts may be the better option.
Consider safety and reliability: Special steam turbines are often used in critical applications where safety and reliability are paramount. If the turbine is showing signs of wear and tear, has a history of failures, or is no longer meeting safety standards, replacement may be necessary.
Consult with experts: It’s important to consult with experts in special steam turbines before making a decision. They can provide guidance on the best course of action based on the specific circumstances of the plant and the turbine.
Develop a maintenance plan: Once a decision has been made to repair or replace a special steam turbine, it’s important to develop a maintenance plan to ensure its continued reliability and availability. This plan should include regular inspections, testing, and maintenance tasks to prevent future failures and unscheduled shutdowns.
Here are some recommendations and actions for how to buy or repair special steam turbines to ensure good reliability, availability, maintainability, and safety in industrial projects and during operational and maintenance issues in an existing plant:
Conduct a thorough assessment: Before making a decision to buy or repair a special steam turbine, it is important to conduct a thorough assessment of the existing turbine’s condition, as well as the operational needs of the plant. This assessment should take into account factors such as the turbine’s age, performance history, maintenance needs, and anticipated lifespan.
Consider the cost-benefit analysis: Once the assessment is complete, a cost-benefit analysis should be performed to determine whether it is more cost-effective to repair the turbine or replace it with a new one. This analysis should consider factors such as the cost of repair, the expected lifespan of the repaired turbine, and the cost of a new turbine.
Choose a reputable supplier: If buying a new special steam turbine, it is important to choose a reputable supplier that has a proven track record of providing reliable and high-quality turbines. Look for suppliers that have experience working with similar industrial projects and that have a reputation for delivering products that meet or exceed industry standards.
Follow manufacturer’s recommendations: When repairing or maintaining a special steam turbine, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance procedures and schedules. This will help ensure that the turbine remains in good working order and that any potential issues are addressed before they can cause critical failures or unscheduled shutdowns.
Use high-quality replacement parts: When repairing a special steam turbine, it is important to use high-quality replacement parts that are designed specifically for the turbine model in question. Using subpar or incompatible parts can lead to poor performance, decreased reliability, and increased risk of critical failures.
Invest in training: To ensure that the special steam turbine is operated and maintained properly, it is important to invest in training for the plant’s staff. This training should cover topics such as turbine operation, maintenance, troubleshooting, and safety. By providing staff with the necessary knowledge and skills, the risk of critical failures and unscheduled shutdowns can be minimized.
The decision on who should buy or repair special steam turbines would depend on the expertise and resources available within the organization. Generally, it is recommended to have specialized and experienced personnel to perform these tasks.
If the organization has in-house expertise and resources to perform maintenance and repair on the special steam turbines, it may be beneficial to repair the turbines rather than buying new ones. This can save money and allow the organization to keep its existing equipment in service for longer periods.
However, if the organization does not have the required expertise and resources, it may be more beneficial to buy new special steam turbines. This can ensure that the equipment is reliable and meets the required specifications and safety standards.
It is recommended to consult with experts in the field and conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis before making a decision on whether to buy or repair special steam turbines. Additionally, regular maintenance and monitoring of the turbines can help to identify any potential issues and prevent critical failures and unscheduled shutdowns.

CRITICAL PROCEDURES & BETTER RECOMMENDATIONS TO BUY OR REPAIR SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
WHEN TO REPAIR OR REPLACE SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
WHAT IS BETTER, REPAIR OR REPLACE SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
Here are some critical procedures and recommendations for special steam turbines to ensure good reliability, availability, maintainability, and safety:
Regular Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance and inspections for the steam turbines to ensure they are in good working condition. This includes checking for any leaks, abnormal vibrations, and signs of wear and tear.
Upgrades and Modernization: Consider upgrading or modernizing the steam turbines with the latest technology to improve efficiency, reliability, and safety. This could include installing condition monitoring systems, upgrading the control system, or replacing obsolete components.
Monitoring and Control: Monitor the performance of the steam turbines using a comprehensive control system. This includes monitoring parameters such as temperature, pressure, and vibration levels to detect any anomalies and potential problems.
Staff Training: Ensure that staff members responsible for operating and maintaining the steam turbines are well trained and have the necessary skills and knowledge to carry out their tasks effectively.
Safety Measures: Implement appropriate safety measures such as interlocks, alarms, and emergency shutdown systems to prevent accidents and protect personnel and equipment.
Regular Testing: Conduct regular testing and performance evaluations of the steam turbines to ensure that they are meeting the required specifications and operating efficiently.
Condition-based Maintenance: Use condition-based maintenance strategies such as predictive maintenance to detect potential problems before they occur, and to optimize maintenance schedules based on the actual condition of the equipment.
Spare Parts Inventory: Maintain an adequate inventory of spare parts to reduce downtime in case of any failures or breakdowns.
Quality Assurance: Ensure that all repairs and maintenance work are carried out by qualified technicians using the appropriate procedures and standards to maintain the reliability and safety of the steam turbines.
By following these critical procedures and recommendations, you can ensure that your special steam turbines have good reliability, availability, maintainability, and safety, and avoid critical failures and unscheduled shutdowns.
The decision to repair or replace a special steam turbine will depend on a number of factors, including the age and condition of the turbine, the cost and availability of replacement parts, and the expected future performance and reliability of the turbine. Here are some recommendations and actions to consider when making this decision:
Regularly monitor the condition of the turbine: By conducting regular inspections and monitoring the performance of the turbine, you can identify any potential issues early and take corrective action before they become more serious. This can help extend the life of the turbine and minimize the need for costly repairs or replacements.
Consider the cost and availability of replacement parts: Before deciding whether to repair or replace a turbine, it’s important to assess the cost and availability of replacement parts. If replacement parts are difficult to obtain or expensive, it may be more cost-effective to repair the turbine.
Evaluate the expected performance and reliability of the turbine: When deciding whether to repair or replace a turbine, it’s important to consider the expected future performance and reliability of the turbine. If the turbine is nearing the end of its expected lifespan and is likely to experience more frequent breakdowns or require more extensive repairs, it may be more cost-effective to replace the turbine rather than continuing to repair it.
Consider the potential impact of downtime: When a turbine breaks down, it can cause significant downtime and lost productivity. It’s important to consider the potential impact of downtime when making the decision to repair or replace a turbine. If the turbine is critical to the operation of the plant or facility and downtime could result in significant losses, it may be more cost-effective to replace the turbine rather than continuing to repair it.
Consult with experts: When making the decision to repair or replace a turbine, it’s important to consult with experts in the field who can provide guidance and advice based on their experience and knowledge. This may include engineers, maintenance professionals, and turbine manufacturers.
In summary, the decision to repair or replace a special steam turbine will depend on a number of factors, and it’s important to carefully consider these factors before making a decision. By monitoring the condition of the turbine, evaluating the cost and availability of replacement parts, assessing the expected performance and reliability of the turbine, considering the potential impact of downtime, and consulting with experts in the field, you can make an informed decision that will help ensure the reliability, availability, maintainability, and safety of your turbine and minimize the risk of critical failures and unscheduled shutdowns.
Deciding whether to repair, replace or buy a special steam turbine depends on various factors, such as the age and condition of the turbine, the cost of repairs, the availability of replacement parts, and the expected future demand for the turbine. Here are some general recommendations and actions to consider:
Assess the condition of the turbine: Determine the age, wear and tear, and overall condition of the turbine. This will help determine whether repairing or replacing the turbine is the best option.
Evaluate the cost of repairs: Get a cost estimate for repairing the turbine, including labor, replacement parts, and any necessary upgrades. Compare this cost to the cost of buying a new or refurbished turbine.
Consider the availability of replacement parts: If the turbine is older, replacement parts may be difficult to find or expensive. This could make it more cost-effective to replace the turbine rather than repair it.
Evaluate the expected future demand for the turbine: Consider the expected demand for the turbine in the future. If the turbine is likely to see increased usage or demand, it may be more cost-effective to replace it with a newer, more efficient model.
Assess the potential impact of downtime: Consider the potential impact of downtime on production and revenue. If repairing the turbine would result in significant downtime, it may be more cost-effective to replace it.
Ultimately, the decision to repair, replace or buy a special steam turbine should be based on a comprehensive evaluation of these factors, as well as any specific considerations related to the plant’s operational and maintenance needs.
ADVANTAGES TO BUY OR REPLACE vs TO REPAIR SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
ADVANTAGES TO REPAIR vs TO REPLACE OR BUY A SPECIAL STEAM TURBINE
There are several advantages to buying or replacing special steam turbines instead of repairing them, particularly in the context of industrial projects and existing plants. Here are some critical advantages to consider:
Improved reliability: New steam turbines are likely to be more reliable than older ones. They incorporate the latest design features and use newer, more advanced materials that are better able to withstand the rigors of heavy industrial use. This means they are less likely to suffer from unexpected breakdowns or other reliability issues.
Increased availability: When a steam turbine fails unexpectedly, it can cause unscheduled shutdowns that disrupt production and reduce overall availability. By investing in new, more reliable equipment, you can reduce the likelihood of these unscheduled shutdowns and improve the overall availability of your plant.
Better maintainability: New steam turbines are often easier to maintain than older ones, particularly if they incorporate modern features like remote monitoring and diagnostics. This means that maintenance tasks can be completed more quickly and efficiently, reducing the risk of extended downtime.
Enhanced safety: Safety is always a top priority in industrial settings, and investing in new steam turbines can help reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. Newer equipment is often designed with safety in mind, incorporating features like automatic shutoffs and fail-safe mechanisms that can help prevent accidents from occurring.
Cost-effective: While the upfront cost of buying or replacing a steam turbine may be higher than repairing an existing one, it can ultimately be more cost-effective in the long run. New equipment is likely to require less maintenance and experience fewer reliability issues, reducing the need for costly repairs and unscheduled shutdowns.
Overall, investing in new, high-quality steam turbines can be an excellent way to improve reliability, availability, maintainability, and safety in industrial settings. By minimizing the risk of unscheduled shutdowns and other reliability issues, you can keep your plant running smoothly and efficiently, ensuring maximum productivity and profitability.
There are also several advantages to repairing special steam turbines instead of buying or replacing them, particularly in the context of industrial projects and existing plants. Here are some critical advantages to consider:
Cost-effective: Repairing a steam turbine can often be more cost-effective than buying or replacing it. This is particularly true if the repairs are minor or if the turbine still has significant useful life left. Repairing the turbine can also be less disruptive to plant operations, as it can often be done on-site without the need to remove the equipment.
Improved reliability: While new steam turbines are generally more reliable than older ones, repairs can often improve the reliability of existing equipment as well. By addressing specific issues and restoring the turbine to its original condition, repairs can help ensure that the turbine continues to operate reliably for many years to come.
Reduced downtime: Repairing a steam turbine can often be faster than buying or replacing it. This means that downtime can be reduced, which is particularly important in industrial settings where unscheduled shutdowns can be costly and disruptive. By quickly repairing the equipment, you can minimize the impact on plant operations and ensure that production continues as scheduled.
Preserves familiarity: Repairing a steam turbine can allow you to maintain the familiarity of your plant’s maintenance team with the equipment. This can be particularly valuable if the plant has specialized or unique equipment that requires specific knowledge and expertise to maintain.
Environmentally friendly: Repairing a steam turbine can be more environmentally friendly than buying or replacing it. This is because manufacturing new equipment requires significant resources and energy, while repairing existing equipment can help extend its useful life and reduce waste.
Overall, there are several critical advantages to repairing special steam turbines in industrial projects and existing plants. By carefully considering the specific needs of your plant and equipment, you can make the best decision about whether to repair, replace, or buy new equipment.
DISADVANTAGES TO REPAIR vs TO BUY OR REPLACE SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
DISADVANTAGES TO BUY OR REPLACE vs TO REPAIR SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
There are several potential disadvantages to repairing rather than replacing or buying special steam turbines:
Cost: While repairing a special steam turbine may seem like the cheaper option upfront, it may end up costing more in the long run if the repairs don’t solve the underlying issues and the turbine continues to experience problems. Additionally, if the turbine is old and outdated, the cost of finding replacement parts for repairs may be much higher than simply buying a new turbine.
Downtime: Repairing a special steam turbine can result in significant downtime for the plant, which can be costly in terms of lost production and revenue. If the repairs take longer than expected, the downtime can be even more substantial.
Safety: Repairing a special steam turbine may not always be the safest option, especially if the repairs involve working on components that are under high pressure or high temperature. This can increase the risk of accidents and injuries for maintenance personnel.
Reliability: Even if repairs are successful in addressing immediate issues with the special steam turbine, there is no guarantee that it will continue to operate reliably in the future. This can lead to unexpected downtime and additional repairs, which can be frustrating and costly for the plant.
Overall, the decision to repair, replace, or buy a special steam turbine should be made based on a careful evaluation of the turbine’s condition, the potential costs and benefits of each option, and the plant’s specific needs and constraints.
Here are some potential disadvantages of buying or replacing special steam turbines instead of repairing them:
Cost: Purchasing a new or replacement steam turbine can be very expensive, especially if it is a specialized model designed for specific processes or environments. On the other hand, repairing a turbine may be more cost-effective in certain cases.
Lead time: If a replacement steam turbine needs to be ordered, there may be a significant lead time before it can be delivered and installed. This can result in lengthy downtime and lost productivity.
Integration with existing systems: If a new or replacement steam turbine is not compatible with existing systems, it may require additional modifications or upgrades to be integrated properly. This can add to the overall cost and complexity of the project.
Environmental impact: The production and disposal of new equipment can have a significant environmental impact, which may be a concern for some organizations.
Training: If a new or replacement steam turbine requires specialized training or expertise to operate and maintain, it may be more challenging to find qualified personnel or require additional investment in training programs.
In certain cases, it may be more advantageous to repair a special steam turbine rather than buying or replacing it, especially if it is a relatively simple repair and the cost and downtime associated with replacing the equipment is significant. However, in other cases, buying or replacing the equipment may be the best course of action to ensure optimal reliability, availability, maintainability, and safety. Ultimately, the decision should be based on a careful analysis of the specific situation, taking into account the potential advantages and disadvantages of each option.
