HOW TO REDUCE RISKS IN ENVIRONMENTAL FAILURES - TURBOMACHINERY
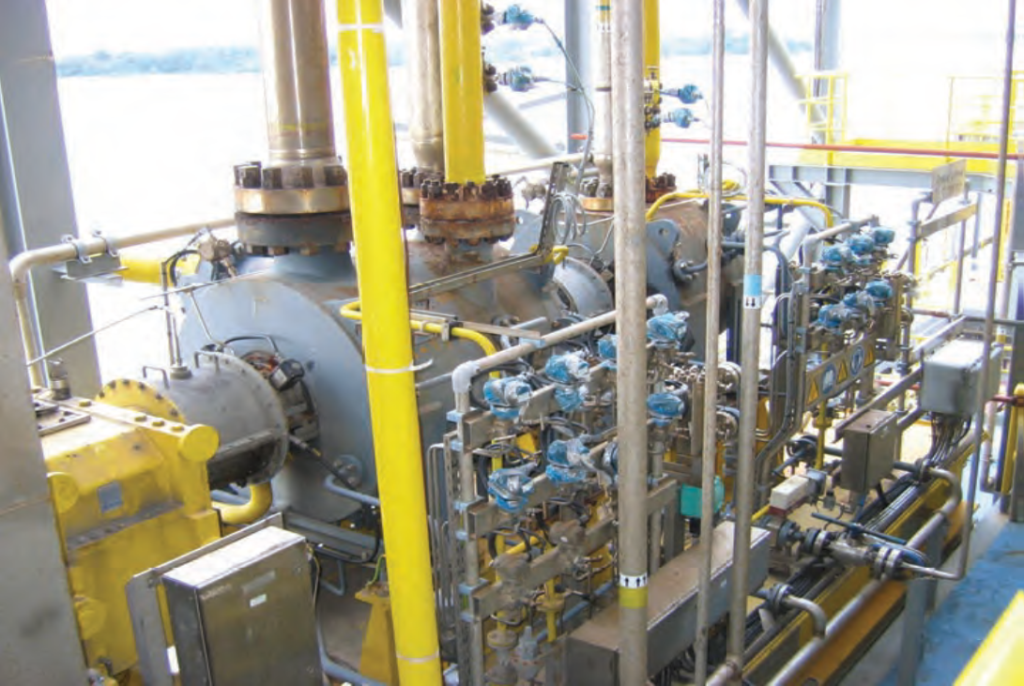

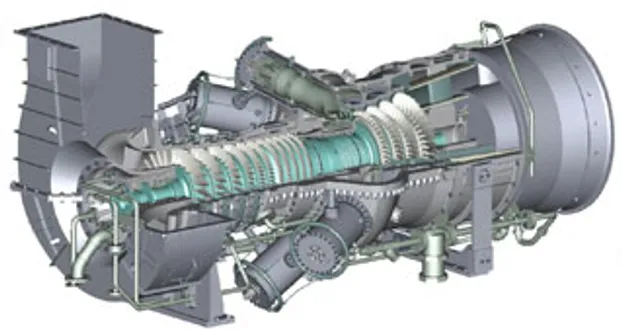

CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS
GAS TURBINES
SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
FREQUENT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS
frequently asked questions and answers related to reducing environmental risks to avoid critical failures or shutdowns in turbomachinery, specifically centrifugal compressors, in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries.
Q: What are the main environmental risks associated with centrifugal compressors in these industries? A: The main environmental risks associated with centrifugal compressors include the release of hazardous gases, liquids or solids into the atmosphere, water or soil, noise pollution, vibration and potential mechanical failure leading to shutdown or catastrophic damage.
Q: How can environmental risks be reduced in the execution of projects involving centrifugal compressors? A: Environmental risks can be reduced in the execution of projects involving centrifugal compressors by performing proper environmental impact assessments (EIAs), adhering to environmental regulations and guidelines, implementing effective monitoring and control measures, and using sustainable design and construction practices.
Q: What can be done to reduce environmental risks in existing operational plants with centrifugal compressors? A: Environmental risks in existing operational plants with centrifugal compressors can be reduced by implementing effective maintenance and inspection programs, identifying and mitigating potential sources of environmental hazards, upgrading outdated equipment with modern, more efficient and environmentally friendly technologies, and improving the training of personnel to enhance their awareness of environmental issues.
Q: How can the risk of mechanical failure in centrifugal compressors be reduced? A: The risk of mechanical failure in centrifugal compressors can be reduced by performing regular maintenance and inspection, using high-quality materials and components, installing effective monitoring and control systems, and implementing a risk-based maintenance strategy.
Q: How can vibration and noise pollution from centrifugal compressors be minimized? A: Vibration and noise pollution from centrifugal compressors can be minimized by using proper installation and alignment techniques, using vibration and noise monitoring and control equipment, selecting low-noise and vibration-resistant components, and implementing effective acoustic insulation and noise control measures.
Q: What are some examples of sustainable design and construction practices for centrifugal compressors? A: Some examples of sustainable design and construction practices for centrifugal compressors include using energy-efficient motors and drives, selecting materials and components with low environmental impact, implementing recycling and waste reduction measures, and designing systems that use renewable energy sources.
GAS TURBINES
some frequently asked questions and answers related to reducing environmental risks to avoid critical failures or shutdowns in turbomachinery, specifically gas turbines, in power generation, oil, gas, and petrochemical industries:
Q: What are the main environmental risks associated with gas turbines in these industries? A: The main environmental risks associated with gas turbines include air pollution from emissions, noise pollution, vibration and potential mechanical failure leading to shutdown or catastrophic damage, and potential oil and fuel spills.
Q: How can environmental risks be reduced in the execution of projects involving gas turbines? A: Environmental risks can be reduced in the execution of projects involving gas turbines by performing proper environmental impact assessments (EIAs), adhering to environmental regulations and guidelines, implementing effective monitoring and control measures, and using sustainable design and construction practices.
Q: What can be done to reduce environmental risks in existing operational plants with gas turbines? A: Environmental risks in existing operational plants with gas turbines can be reduced by implementing effective maintenance and inspection programs, identifying and mitigating potential sources of environmental hazards, upgrading outdated equipment with modern, more efficient, and environmentally friendly technologies, and improving the training of personnel to enhance their awareness of environmental issues.
Q: How can the risk of mechanical failure in gas turbines be reduced? A: The risk of mechanical failure in gas turbines can be reduced by performing regular maintenance and inspection, using high-quality materials and components, installing effective monitoring and control systems, and implementing a risk-based maintenance strategy.
Q: How can emissions and air pollution from gas turbines be reduced? A: Emissions and air pollution from gas turbines can be reduced by implementing emissions control technologies such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), using low-emission fuels, and improving combustion efficiency through optimized designs and control systems.
Q: What are some examples of sustainable design and construction practices for gas turbines? A: Some examples of sustainable design and construction practices for gas turbines include using energy-efficient components and systems, selecting materials and components with low environmental impact, implementing recycling and waste reduction measures, and designing systems that use renewable energy sources such as wind or solar power.
Q: How can noise pollution and vibration from gas turbines be minimized? A: Noise pollution and vibration from gas turbines can be minimized by using proper installation and alignment techniques, using vibration and noise monitoring and control equipment, selecting low-noise and vibration-resistant components, and implementing effective acoustic insulation and noise control measures.
SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
some frequently asked questions and answers related to reducing environmental risks to avoid critical failures or shutdowns in special steam turbines, in power generation, oil, gas, and petrochemical industries:
Q: What are the main environmental risks associated with special steam turbines in these industries? A: The main environmental risks associated with special steam turbines include air pollution from emissions, water pollution from potential leaks or spills, noise pollution, vibration and potential mechanical failure leading to shutdown or catastrophic damage.
Q: How can environmental risks be reduced in the execution of projects involving special steam turbines? A: Environmental risks can be reduced in the execution of projects involving special steam turbines by performing proper environmental impact assessments (EIAs), adhering to environmental regulations and guidelines, implementing effective monitoring and control measures, and using sustainable design and construction practices.
Q: What can be done to reduce environmental risks in existing operational plants with special steam turbines? A: Environmental risks in existing operational plants with special steam turbines can be reduced by implementing effective maintenance and inspection programs, identifying and mitigating potential sources of environmental hazards, upgrading outdated equipment with modern, more efficient, and environmentally friendly technologies, and improving the training of personnel to enhance their awareness of environmental issues.
Q: How can the risk of mechanical failure in special steam turbines be reduced? A: The risk of mechanical failure in special steam turbines can be reduced by performing regular maintenance and inspection, using high-quality materials and components, installing effective monitoring and control systems, and implementing a risk-based maintenance strategy.
Q: How can emissions and air pollution from special steam turbines be reduced? A: Emissions and air pollution from special steam turbines can be reduced by implementing emissions control technologies such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), using low-emission fuels, and improving combustion efficiency through optimized designs and control systems.
Q: How can water pollution from special steam turbines be minimized? A: Water pollution from special steam turbines can be minimized by implementing effective water management systems, including wastewater treatment and reuse, and by ensuring that all materials and fluids used in the turbine are properly contained and disposed of.
Q: What are some examples of sustainable design and construction practices for special steam turbines? A: Some examples of sustainable design and construction practices for special steam turbines include using energy-efficient components and systems, selecting materials and components with low environmental impact, implementing recycling and waste reduction measures, and designing systems that use renewable energy sources such as biomass or geothermal power.
Q: How can noise pollution and vibration from special steam turbines be minimized? A: Noise pollution and vibration from special steam turbines can be minimized by using proper installation and alignment techniques, using vibration and noise monitoring and control equipment, selecting low-noise and vibration-resistant components, and implementing effective acoustic insulation and noise control measures.
