SCHEDULED vs NON SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE IN TURBOMACHINERY
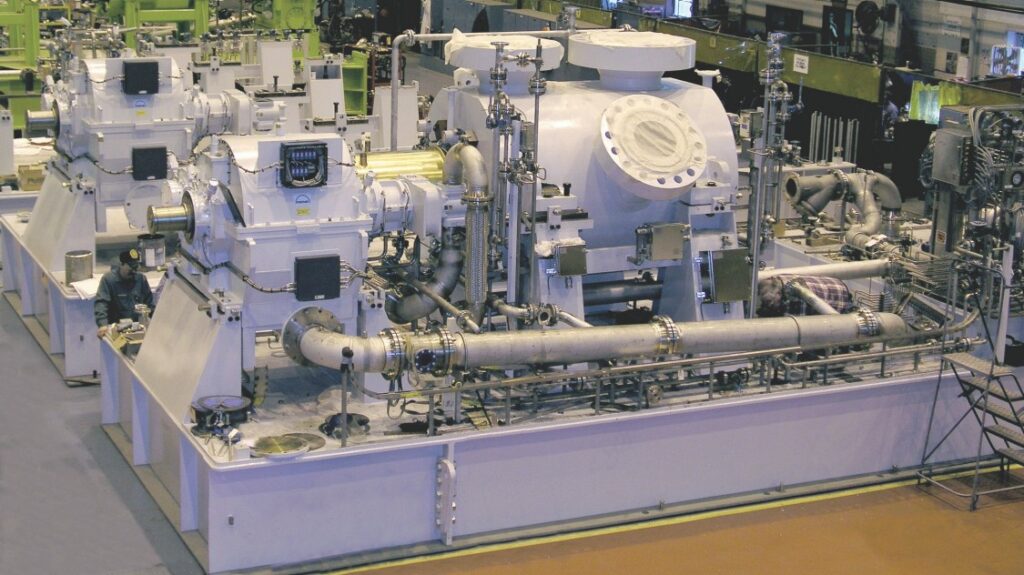

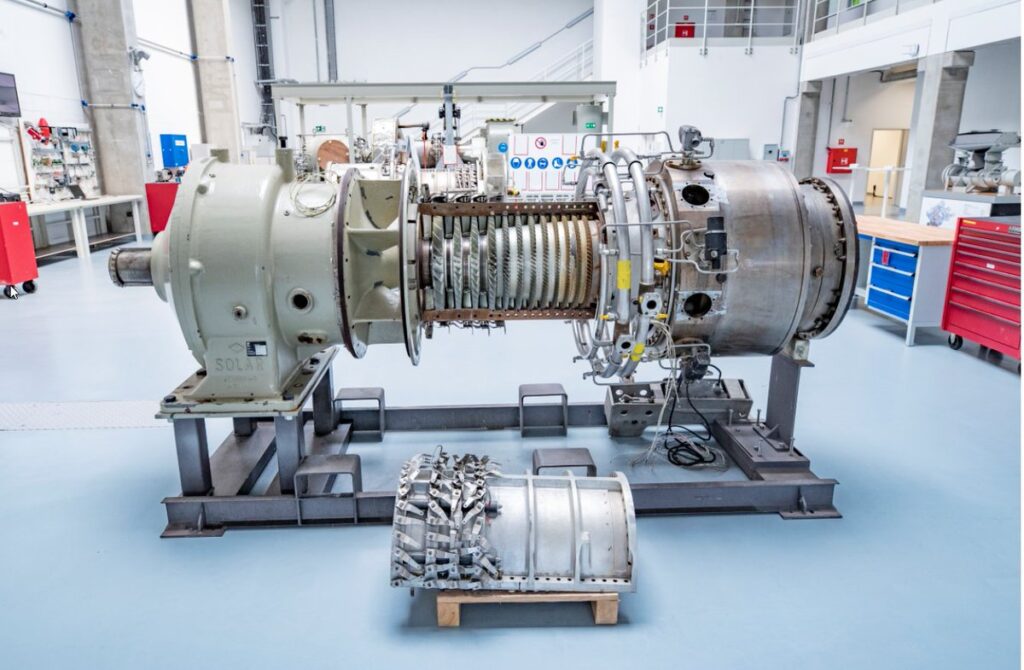
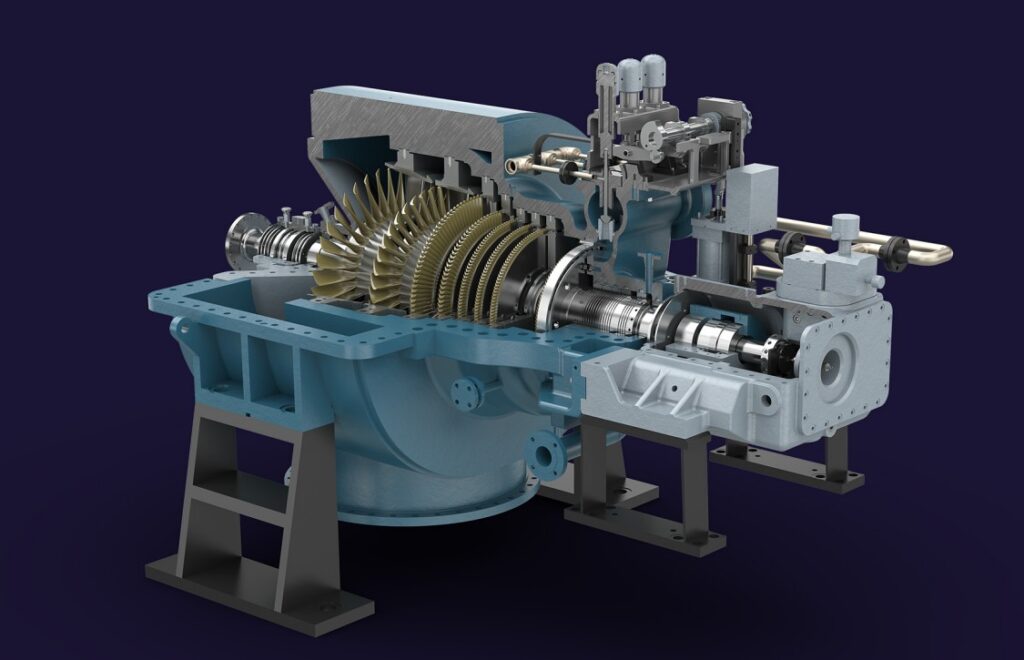
CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS
GAS TURBINES
SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
IMPACTS IN RELIABILITY & COSTS ASSOCIATED WITH SCHEDULED vs NON SCHEDULED SHUTDOWNS IN TURBOMACHINERY
Reliability Impacts:
Scheduled Shutdowns:
- Centrifugal Compressors: Scheduled shutdowns provide an opportunity to inspect, clean, and maintain critical components such as impellers, casings, seals, and bearings. This helps prevent issues like fouling, erosion, and mechanical wear, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
- Gas Turbines: Scheduled shutdowns allow for inspections, cleaning, and replacement of worn-out components such as blades, combustion chambers, fuel nozzles, and filters. This helps maintain turbine efficiency, combustion stability, and overall reliability.
- Special Steam Turbines: Scheduled shutdowns facilitate maintenance activities such as blade inspections, turbine alignment, lubrication system checks, and valve maintenance. These activities help prevent steam leakage, blade erosion, and mechanical failures, ensuring reliable operation.
Non-scheduled Shutdowns:
- Centrifugal Compressors: Non-scheduled shutdowns due to unexpected failures can result in prolonged downtime, emergency repairs, and potential collateral damage to other equipment. This can negatively impact compressor reliability, increase repair costs, and disrupt operations.
- Gas Turbines: Non-scheduled shutdowns in gas turbines can be caused by various factors such as component failures, control system issues, or fuel supply problems. These shutdowns can lead to higher repair costs, longer downtime, and potential risks to other plant assets.
- Special Steam Turbines: Non-scheduled shutdowns in steam turbines may occur due to issues like steam leakage, valve malfunctions, or turbine trips. These shutdowns can result in costly repairs, production losses, and compromised reliability.
Cost Impacts:
Scheduled Shutdowns:
- Centrifugal Compressors: While scheduled shutdowns require temporary cessation of operations, they can help reduce costs in the long run. By addressing potential issues, performing preventive maintenance, and optimizing compressor performance, the risk of unexpected breakdowns, emergency repairs, and associated costs is minimized.
- Gas Turbines: Scheduled shutdowns enable planned maintenance activities, such as component replacements, inspections, and performance optimization. This helps extend the turbine’s lifespan, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce long-term maintenance and fuel costs.
- Special Steam Turbines: Scheduled shutdowns allow for planned maintenance activities, such as blade inspections, valve maintenance, and lubrication system checks. These activities contribute to optimized turbine performance, enhanced reliability, and reduced long-term maintenance costs.
Non-scheduled Shutdowns:
- Centrifugal Compressors: Non-scheduled shutdowns due to unexpected failures can result in higher repair costs, rush orders for spare parts, overtime wages, and potential production losses. These costs can significantly impact the overall plant budget and profitability.
- Gas Turbines: Non-scheduled shutdowns in gas turbines can lead to expensive emergency repairs, replacement part costs, downtime losses, and potential penalties for not meeting contractual obligations. These costs can have a substantial impact on the plant’s financial performance.
- Special Steam Turbines: Non-scheduled shutdowns in steam turbines can result in unplanned maintenance expenses, production interruptions, potential damage to other equipment, and revenue losses. These costs can negatively affect the plant’s operational budget.
In summary, scheduled shutdowns play a crucial role in maintaining reliability and reducing costs in centrifugal compressors, gas turbines, and special steam turbines in power generation, oil, and gas industries. By conducting planned maintenance activities, addressing potential issues, and optimizing performance, the risk of critical failures, associated risks, and costly repairs can be minimized. On the other hand, non-scheduled shutdowns due to unexpected failures can have adverse impacts on reliability, increase repair costs, and disrupt operations, thereby impacting the plant’s overall cost-effectiveness.
WHY, WHEN, WHERE, WHAT, WHICH AND HOW TO INCREASE RELIABILITY ABOUT THE SCHEDULED vs NON-SCHEDULED SHUTDOWNS IN TURBOMACHINERY
WHY:
- Increasing Reliability: Enhancing reliability in these equipment ensures uninterrupted operation, reduces the risk of critical failures, minimizes downtime, and improves overall plant efficiency and productivity.
- Reducing Costs: By implementing effective maintenance strategies, optimizing performance, and avoiding unexpected failures, costs associated with emergency repairs, replacement parts, downtime, and lost production can be minimized, leading to cost savings.
WHEN:
Scheduled Shutdowns:
- Centrifugal Compressors: Schedule maintenance activities based on equipment manufacturer recommendations, historical data, operating hours, and condition monitoring results. Consider factors such as compressor usage, environmental conditions, and maintenance intervals to determine the appropriate frequency of scheduled shutdowns.
- Gas Turbines: Plan scheduled shutdowns based on recommended maintenance intervals, operating hours, and maintenance history. Consider factors such as fuel quality, operating environment, and maintenance requirements specific to gas turbines.
- Special Steam Turbines: Schedule maintenance based on manufacturer guidelines, operational hours, historical data, and condition monitoring results. Consider factors such as steam quality, operating conditions, and specific maintenance requirements for steam turbines.
Non-scheduled Shutdowns:
- Respond to non-scheduled shutdowns promptly when equipment failures, abnormal conditions, or safety concerns arise. Address the issues based on their criticality and impact on operations.
WHERE:
Scheduled Shutdowns:
- Centrifugal Compressors: Address the entire compressor system, including impellers, casings, seals, bearings, lubrication systems, and associated equipment.
- Gas Turbines: Focus on critical components such as blades, combustion chambers, fuel nozzles, filters, lubrication systems, and control systems.
- Special Steam Turbines: Address critical components, including blades, valves, turbine casings, lubrication systems, and governing systems.
Non-scheduled Shutdowns:
- Address the specific component or system that has experienced the failure or poses a risk to safe and reliable operation.
WHAT:
Scheduled Shutdowns:
- Conduct inspections, cleaning, maintenance, and component replacements as per manufacturer guidelines and industry best practices.
- Focus on tasks such as blade inspections, seal replacements, lubrication system checks, and alignment verification.
- Verify and optimize performance parameters, such as efficiency, pressure ratios, and temperature differentials.
Non-scheduled Shutdowns:
- Perform troubleshooting, root cause analysis (RCA), and take appropriate corrective actions to resolve the specific issue and prevent future recurrences.
WHICH:
Scheduled Shutdowns:
- Identify critical components and systems that require maintenance or replacement based on factors such as maintenance history, failure modes, and condition monitoring results.
- Prioritize maintenance activities for high-risk components, such as impellers, blades, seals, and control systems.
Non-scheduled Shutdowns:
- Focus on the specific component or system that has failed or poses a safety risk. Address the root cause of the failure and implement appropriate corrective actions.
HOW:
Scheduled Shutdowns:
- Plan scheduled shutdowns well in advance to allocate resources, coordinate with suppliers, and minimize impact on operations.
- Develop detailed maintenance plans, including schedules, tasks, and responsibilities.
- Utilize computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) to track maintenance activities, manage work orders, and maintain maintenance records.
Non-scheduled Shutdowns:
- Establish an efficient emergency response system that includes rapid communication, a clear escalation process, and access to necessary resources.
- Conduct root cause analysis (RCA) to identify the underlying causes of failures and implement appropriate corrective measures.
- Update maintenance plans and procedures based on lessons learned from non-scheduled shutdowns to improve future response and prevent similar incidents.
By focusing on these aspects, power generation, oil, and gas industries can increase the reliability and reduce costs in centrifugal compressors, gas turbines, and special steam turbines. This helps to avoid critical failures, minimize risks, optimize maintenance activities, and ensure efficient and cost-effective operation of the equipment.


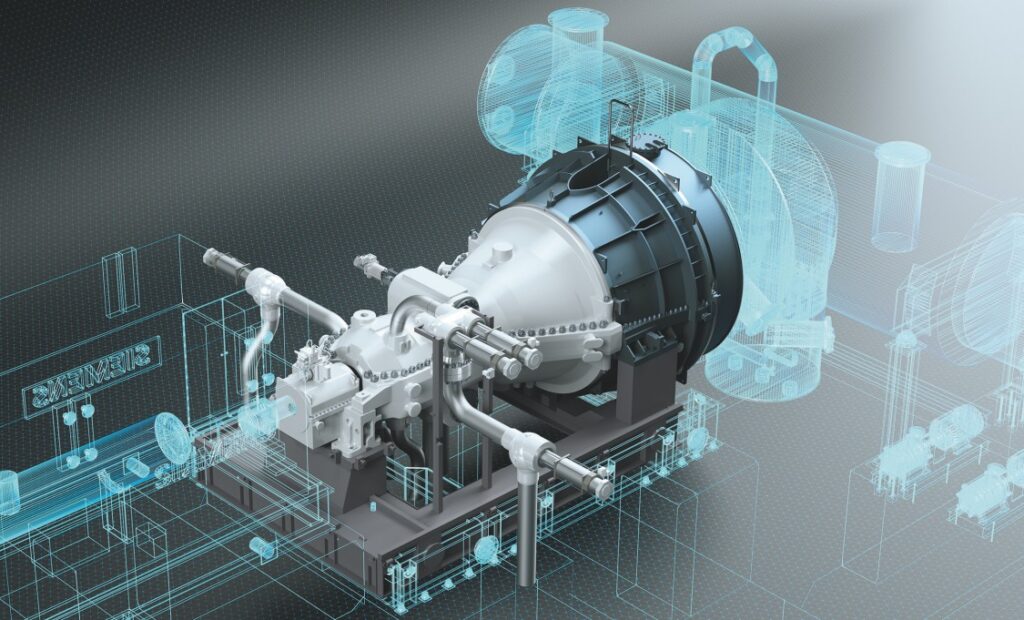
PROCEDURES, ACTIONS, STUDIES, MITIGATIONS, RECOMMENDATIONS TO INCREASE THE RELIABILITY IN TURBOMACHINERY RELATED TO SCHEDULED vs NON-SCHEDULED SHUTDOWNS
Procedures and Actions:
- Develop a comprehensive maintenance plan that includes scheduled shutdowns for inspections, cleaning, and maintenance activities, such as component replacements, lubrication system checks, and performance optimization.
- Implement condition-based maintenance techniques, such as vibration analysis, thermography, oil analysis, and performance monitoring, to detect early signs of potential failures and schedule maintenance accordingly.
- Regularly inspect and clean critical components, such as impellers, blades, casings, seals, lubrication systems, combustion chambers, and valves, to prevent fouling, erosion, and mechanical wear.
- Optimize operational parameters, such as pressure ratios, temperature differentials, and efficiency, to ensure reliable and efficient performance.
- Utilize remote monitoring and diagnostics to enable real-time monitoring of operational parameters, identify abnormalities, and take proactive actions.
Studies and Assessments:
- Perform reliability assessments and failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) studies to identify critical components, failure modes, their impacts, and appropriate mitigation strategies.
- Conduct root cause analysis (RCA) for critical failures and non-scheduled shutdowns to identify the underlying causes and develop effective corrective measures.
- Perform lifecycle cost analysis to identify areas where cost reductions can be achieved without compromising reliability and safety.
Mitigations:
- Establish a comprehensive spare parts inventory and ensure timely availability of critical components to minimize downtime during both scheduled and non-scheduled shutdowns.
- Implement a proactive maintenance strategy, such as condition-based maintenance, predictive maintenance, and reliability-centered maintenance (RCM) practices, to optimize maintenance activities and prevent unexpected failures.
- Implement robust monitoring and control systems to detect abnormal operating conditions and initiate appropriate actions to prevent equipment damage.
- Develop contingency plans and emergency response procedures to minimize downtime and ensure swift resolution of non-scheduled shutdowns.
Recommendations:
- Implement a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) to track maintenance activities, manage work orders, and analyze maintenance data for continuous improvement.
- Foster a culture of safety, reliability, and continuous improvement through training programs, regular knowledge sharing sessions, and cross-functional collaboration.
- Regularly review and update maintenance procedures and protocols based on lessons learned from previous shutdowns, maintenance activities, and failure incidents.
- Establish strong relationships with equipment manufacturers, suppliers, and service providers to leverage their expertise, access technical support, and stay updated on maintenance best practices.
- Invest in advanced technologies, such as predictive analytics, IoT-enabled sensors, and machine learning algorithms, to further optimize maintenance strategies and enhance reliability.
By following these procedures, taking appropriate actions, conducting relevant studies and assessments, implementing mitigations, and incorporating the recommendations, power generation, oil, and gas industries can increase reliability and reduce costs in centrifugal compressors, gas turbines, and special steam turbines. This will help avoid critical failures, minimize risks, optimize maintenance activities, and ensure efficient and cost-effective operation of the equipment.
