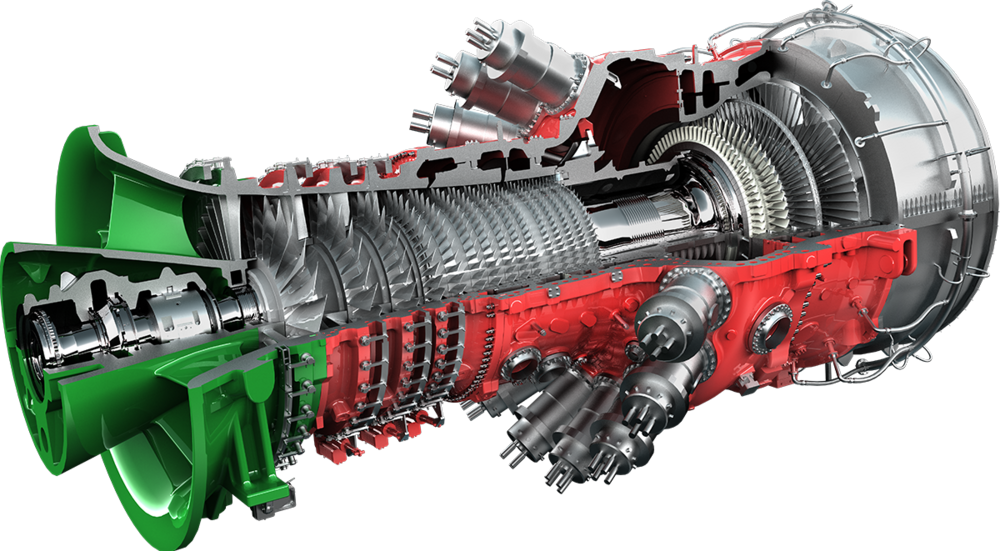
MAINTAINABILITY vs SPARE PARTS PHILOSOPHY - GAS TURBINES
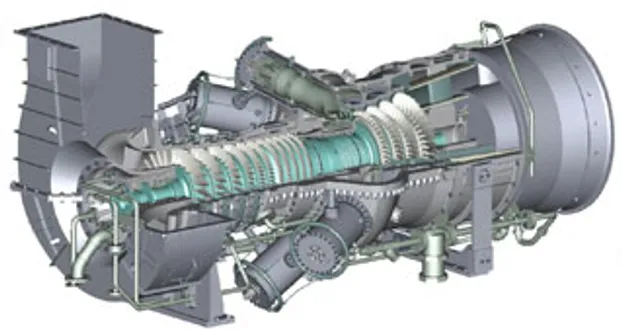
WHAT IF WE DON'T HAVE IMPLEMENTED A SPARE PARTS PHILOSOPHY AND HOW COULD AFFECT THE MAINTAINABILITY - GAS TURBINES
The maintainability of gas turbines is critical to ensure their reliability and availability in industrial plants, such as in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries. Failure to properly maintain gas turbines can lead to unscheduled shutdowns, costly repairs, and lost productivity. A spare parts philosophy is crucial to ensuring proper maintenance and reducing the risk of critical failures.
If a spare parts philosophy has not been implemented, the following issues may arise:
Downtime: Without proper spare parts, any maintenance required on a gas turbine will take longer, resulting in extended downtime and lost productivity.
Repair costs: In the event of a critical failure, the cost of repair may be higher if spare parts are not readily available. Waiting for parts to be shipped can also delay the repair process, resulting in further lost productivity.
Safety risks: Inadequate maintenance can lead to safety risks for workers, equipment, and the environment. Having spare parts readily available can help ensure maintenance is performed on time, reducing the likelihood of accidents and equipment failures.
To ensure a very good timing about maintainability in gas turbines, it is important to have a spare parts philosophy in place. This includes the following actions:
Inventory management: Develop a system for tracking inventory and ensure that all critical spare parts are kept in stock. Consider factors such as lead time and usage rates to determine appropriate inventory levels.
Preventative maintenance: Conduct regular preventative maintenance on gas turbines to catch potential issues before they become critical failures. Ensure that maintenance schedules are adhered to and that all necessary spare parts are available for the maintenance work.
Training and skills development: Provide training and skills development for maintenance personnel to ensure they have the knowledge and expertise required to maintain gas turbines properly.
Collaboration with suppliers: Work closely with gas turbine suppliers to ensure that spare parts are readily available and that lead times are minimized. Consider implementing service agreements to ensure that parts are delivered in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Continuous improvement: Regularly review and update the spare parts philosophy to ensure that it is effective and aligned with the organization’s goals and objectives.
WHY, WHERE, WHEN, WHO, HOW TO IMPLEMENT A SPARE PARTS PHILOSOPHY IN ORDER TO IMPROVE THE MAINTAINABILITY IN GAS TURBINES
A spare parts philosophy is crucial for achieving high maintainability and availability in gas turbines. Here are the reasons, timing, and recommended actions for implementing a spare parts philosophy:
WHY: Gas turbines are complex machines that require regular maintenance and occasional repair or replacement of components. Having spare parts readily available reduces the time required to perform maintenance or repairs and minimizes downtime. It also ensures that the correct parts are available when needed, reducing the risk of using incorrect or incompatible parts that could lead to further problems.
WHEN: A spare parts philosophy should be implemented as soon as possible when operating gas turbines in an industrial plant, as this reduces the risk of unscheduled downtime and critical failures.
WHO: The spare parts philosophy should be implemented by a team of experienced engineers, maintenance personnel, and procurement specialists who are knowledgeable about gas turbine components and maintenance requirements.
HOW: The following steps are recommended for implementing a spare parts philosophy in gas turbines:
- Conduct a comprehensive analysis of the gas turbine’s components and identify critical components that require spares.
- Develop a spare parts inventory management system that includes a list of all critical components, their current inventory levels, and their expected lifetimes.
- Establish a reliable supply chain for the spare parts, either through in-house procurement or partnerships with reliable suppliers.
- Ensure that the spare parts are stored in a secure, climate-controlled location to prevent damage or degradation.
- Develop a regular maintenance and inspection schedule to ensure that spare parts are in good working condition when needed.
- WHERE: A spare parts philosophy should be implemented at the industrial plant where the gas turbine is operating, as this is where the spare parts will be needed.
In the case of not having a spare parts availability in stock, gas turbine maintenance or repair may be delayed or even postponed, resulting in unscheduled downtime, critical failures, and potentially higher repair costs due to expedited shipping or rush orders. This can also result in reduced availability and reliability of the gas turbine, negatively impacting overall plant operations. Therefore, it is critical to implement a spare parts philosophy to ensure that spare parts are readily available when needed.
PROCEDURES AND RECOMMENDATIONS TO IMPLEMENT A SPARE PARTS PHILOSOPHY IN ORDER TO IMPROVE THE MAINTAINABILITY AND AVAILABILITY
Implementing a spare parts philosophy for gas turbines requires careful planning and execution. Here are some recommended procedures and technical recommendations:
Inventory Management: Conduct an inventory of all critical and non-critical spare parts required for the gas turbine. Identify the lead time and the frequency of use of each spare part.
Criticality Assessment: Conduct a criticality assessment of each spare part to determine the level of priority in stock management.
Supply Chain Management: Implement a robust supply chain management system to ensure a steady flow of spare parts to the plant. This should include identifying and qualifying suppliers, establishing clear communication channels, and developing contingency plans for potential disruptions in the supply chain.
Lifecycle Cost Analysis: Perform a lifecycle cost analysis to determine the most cost-effective strategy for maintaining an appropriate level of spare parts in stock. This analysis should consider the cost of downtime, the cost of holding inventory, and the cost of acquiring spare parts.
Storage Management: Establish proper storage conditions for spare parts to ensure they remain in good condition until needed. This should include implementing a suitable inventory management system, proper labeling, and storage location identification.
Maintenance and Inspection: Conduct regular inspections and maintenance of spare parts to ensure they are still usable and in good condition.
Training and Education: Train and educate personnel responsible for spare parts management on proper inventory management techniques and procedures.
Continuous Improvement: Continuously review and evaluate the effectiveness of the spare parts management program to identify areas for improvement and optimize the inventory management system.
By following these procedures and recommendations, it is possible to implement an effective spare parts philosophy for gas turbines that can help ensure better maintainability, availability, and reduced critical failures or unscheduled shutdowns in existing plants of oil, gas, and petrochemical industries.

FREQUENT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS IN THE INDUSTRY ABOUT MAINTAINABILITY vs SPARE PARTS PHILOSOPHY - GAS TURBINES
Here are some frequently asked questions and answers about maintainability and spare parts philosophy specifically related to gas turbines in oil, gas, and petrochemical industries:
Q: What are gas turbines? A: Gas turbines are combustion engines that use compressed air and fuel to generate power for various applications, such as power generation, oil and gas processing, and petrochemical production.
Q: Why is maintainability important for gas turbines? A: Maintaining gas turbines efficiently and effectively is crucial to minimize downtime and ensure the availability of power and other critical services in oil, gas, and petrochemical industries.
Q: What is a spare parts philosophy for gas turbines? A: A spare parts philosophy for gas turbines is a strategy that ensures the availability of critical spare parts for these turbines to reduce downtime and ensure reliability.
Q: What are some factors to consider when implementing a spare parts philosophy for gas turbines? A: Some factors to consider include identifying the critical spare parts required for the specific turbine model, setting stock levels based on lead time and frequency of usage, continuously monitoring and updating inventory levels, and ensuring effective communication between maintenance and procurement departments.
Q: How can users and clients ensure good maintainability of gas turbines? A: Users and clients can ensure good maintainability of gas turbines by implementing a preventive maintenance program, performing regular inspections and maintenance, using high-quality parts and lubricants, investing in training for maintenance staff, and continuously monitoring and updating inventory levels of critical spare parts.
Q: What are some potential consequences of not having a spare parts philosophy in place for gas turbines? A: Not having a spare parts philosophy in place for gas turbines can result in critical failures, unscheduled shutdowns, and prolonged downtime, which can lead to significant losses in production, revenue, and safety.
Q: How can technology help improve maintainability and spare parts management for gas turbines? A: Technology such as predictive maintenance systems, asset management software, and remote monitoring can help to improve maintenance efficiency, reduce downtime, and ensure the availability of critical spare parts for gas turbines.
Q: What are some procedures and recommendations to improve the maintainability due to have or not a spare parts philosophy in case of gas turbines, in order to reduce critical failures, in oil, gas, and petrochemical industries? A: Some procedures and recommendations to improve maintainability and reduce critical failures in gas turbines in oil, gas, and petrochemical industries include implementing a preventive maintenance program, performing regular inspections and maintenance, using high-quality parts and lubricants, investing in training for maintenance staff, continuously monitoring and updating inventory levels of critical spare parts, implementing a spare parts philosophy, and utilizing technology such as predictive maintenance systems, asset management software, and remote monitoring.