OREDA STUDIES - CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS

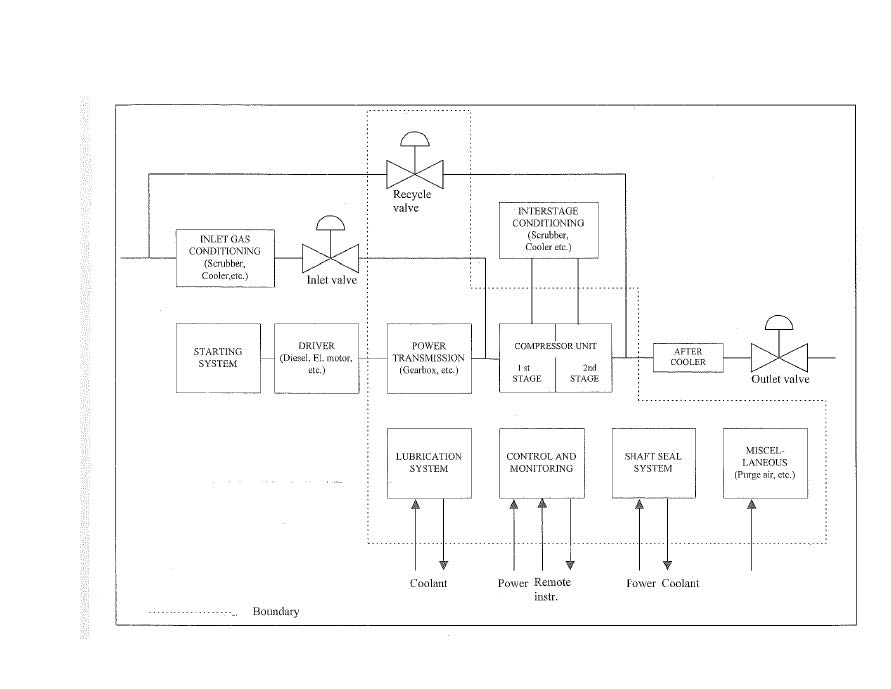
PROCEDURES, ACTIONS, STUDIES, MITIGATIONS, RECOMMENDATIONS
CRITICAL RISKS & FAILURES EVALUATED FOR CENTRIFUGAL COPRESSORS
The OREDA (Offshore and Onshore Reliability Data) studies provide a wealth of information on best practices for improving the reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety of machinery in the oil and gas industries. Here are some of the procedures, actions, studies, mitigation measures, conclusions, and recommendations that can be gleaned from the OREDA data:
Maintenance: The OREDA handbooks provide guidance on best practices for maintenance, including recommendations for routine maintenance activities such as cleaning, inspection, lubrication, and replacement of worn or damaged parts. The data also provides information on maintenance intervals, repair times, and spare parts inventory management.
Monitoring: The OREDA handbooks provide information on various monitoring techniques, such as vibration monitoring, oil analysis, and thermography, that can be used to detect and diagnose machinery problems before they lead to critical failures. The data also provides information on the frequency and severity of different types of machinery failures, and the recommended monitoring frequencies for different types of equipment.
Mitigation: The OREDA data provides information on various mitigation measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of machinery failures, including improved design practices, improved materials selection, and the use of advanced monitoring and diagnostic tools.
Conclusions and Recommendations: Based on the data collected in the OREDA studies, the handbooks provide conclusions and recommendations for improving the reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety of machinery in the oil and gas industries. These recommendations may include changes to design specifications, changes to maintenance procedures, and changes to operational practices.
In general, the OREDA studies provide a comprehensive and data-driven approach to improving the reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety of machinery in the oil and gas industries. By implementing the recommended best practices for maintenance, monitoring, and mitigation, companies can reduce the risk of critical, degraded, and incipient failures and improve the overall performance of their machinery. It is important to balance the time required for maintenance and repair with operational requirements, to ensure optimal equipment reliability and safety.
The OREDA (Offshore and Onshore Reliability Data) studies evaluate various types of risks and failures associated with centrifugal compressors, as well as other machinery used in the oil and gas industries. These risks and failures can be broadly classified into three categories:
Critical Failures: These are failures that result in the immediate shutdown of the machinery or process. Examples of critical failures for centrifugal compressors may include catastrophic failure of a rotor or impeller, bearing failure, or seal failure. Such failures can have significant safety and financial consequences, including the risk of fire, explosion, or release of hazardous materials.
Degradation Failures: These are failures that occur over time due to wear and tear, corrosion, or other factors. Examples of degradation failures for centrifugal compressors may include erosion of compressor blades, fouling of heat exchangers, or degradation of lubricant properties. Such failures can lead to reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, and reduced equipment life.
Incipient Failures: These are failures that are not immediately apparent but may develop into critical or degradation failures if left unchecked. Examples of incipient failures for centrifugal compressors may include vibration or noise anomalies, abnormal temperatures or pressures, or changes in lubricant properties. Detection and diagnosis of incipient failures through proper monitoring and maintenance practices can prevent more severe failures from occurring.
By evaluating and mitigating these types of failures, the OREDA studies aim to improve the reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety of machinery in the oil and gas industries. The data and recommendations provided by the studies can help companies identify critical risks and failure modes, implement effective maintenance and monitoring practices, and reduce the risk of catastrophic or costly failures. It is important to consider the maintenance repair time required for each identified risk and failure, to ensure that maintenance activities can be performed efficiently and effectively without adversely affecting operational requirements.
WHY, WHEN, WHERE, WHAT, WHICH, HOW TO APPLY OREDA IN CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS
OREDA (Offshore Reliability Data) is a well-known industry database that collects and analyzes reliability and maintenance data for offshore oil and gas equipment. Although it primarily focuses on offshore installations, its principles and methodologies can also be applied to onshore plants in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries to improve reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety. Let’s break down your questions:
Why apply OREDA studies and analysis for centrifugal compressors?
- OREDA studies provide valuable insights into the performance and failure modes of various equipment, including centrifugal compressors. By applying OREDA data and analysis, you can gain a better understanding of the reliability issues and failure patterns specific to centrifugal compressors. This knowledge enables you to make informed decisions regarding maintenance strategies, equipment design, and operational practices, ultimately improving reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety.
When should OREDA studies and analysis be applied?
- OREDA studies and analysis can be applied at various stages, including during the design phase, equipment procurement, installation, and throughout the operational lifecycle. Ideally, it is beneficial to incorporate OREDA data early in the design process to inform equipment selection and design decisions. However, even in existing plants, conducting periodic assessments using OREDA studies can help identify areas for improvement and optimize maintenance practices.
Where should OREDA studies and analysis be applied?
- OREDA studies and analysis can be applied in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries, both onshore and offshore. For existing plants, it is particularly relevant in facilities that utilize centrifugal compressors, such as refineries, gas processing plants, and petrochemical plants. The insights gained from OREDA data can be used to enhance the reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety of centrifugal compressors in these installations.
What can be achieved by applying OREDA studies and analysis?
- By applying OREDA studies and analysis for centrifugal compressors, you can achieve several benefits:
- Improved reliability: OREDA data helps identify common failure modes and root causes, allowing you to implement proactive maintenance strategies to mitigate those issues.
- Enhanced maintainability: OREDA studies provide information on the frequency and duration of maintenance activities, enabling you to optimize maintenance schedules, spare parts management, and procedures.
- Increased availability: By addressing reliability and maintainability issues, you can reduce unplanned downtime, leading to increased availability and improved production efficiency.
- Enhanced safety: OREDA studies can help identify safety-critical components and failure modes, allowing you to implement appropriate safeguards and risk mitigation measures.
- By applying OREDA studies and analysis for centrifugal compressors, you can achieve several benefits:
Which specific aspects of OREDA studies should be considered for centrifugal compressors?
- When applying OREDA studies to centrifugal compressors, consider the following aspects:
- Failure data analysis: Analyze failure rates, failure modes, and causes specific to centrifugal compressors. This information can guide reliability improvement efforts.
- Maintenance data analysis: Assess maintenance activities, intervals, and durations to optimize maintenance practices and reduce downtime.
- Common cause analysis: Identify common causes of failures and implement measures to address those issues systematically.
- Risk assessment: Evaluate safety-critical components, potential hazards, and associated risks. Use this information to implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies.
- Benchmarking: Compare your plant’s performance against industry data to identify performance gaps and target areas for improvement.
- When applying OREDA studies to centrifugal compressors, consider the following aspects:
How to apply OREDA studies and analysis for centrifugal compressors?
- To apply OREDA studies and analysis for centrifugal compressors, follow these steps:
Access OREDA Data: Obtain access to the OREDA database or relevant publications. This will provide you with valuable industry data on centrifugal compressor reliability, failure modes, and maintenance practices.
Collect Plant-Specific Data: Gather relevant data specific to your existing plant’s centrifugal compressors. This includes historical maintenance records, failure data, operational parameters, and any available performance data.
Identify Failure Modes: Analyze the failure data collected from your plant to identify common failure modes specific to centrifugal compressors. Compare this data with the OREDA database to determine if your plant experiences similar failure patterns.
Root Cause Analysis: Perform a root cause analysis for identified failure modes. Investigate the underlying causes of failures, such as design issues, material degradation, operating conditions, or maintenance practices. This analysis helps you understand the factors contributing to reliability issues.
Review Maintenance Practices: Evaluate your plant’s current maintenance practices and procedures for centrifugal compressors. Compare them with industry best practices and recommendations derived from the OREDA data. Identify any gaps or areas for improvement.
Optimize Maintenance Strategies: Based on the findings from the OREDA data and your plant-specific analysis, develop and implement optimized maintenance strategies. This includes determining appropriate maintenance intervals, tasks, and procedures. Consider implementing condition-based or predictive maintenance techniques to maximize reliability and minimize downtime.
Spare Parts Management: Assess your spare parts inventory management for centrifugal compressors. Utilize the OREDA data and industry insights to optimize your spare parts strategy, ensuring that critical components are readily available when needed.
Implement Safety Measures: Utilize the OREDA data to identify safety-critical components and failure modes. Evaluate your plant’s existing safety measures and compare them with industry recommendations. Implement appropriate safeguards and risk mitigation measures to enhance safety.
Monitor and Evaluate: Establish a system for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of your centrifugal compressor performance. Continuously collect and analyze data on failures, maintenance activities, and equipment condition. Compare your plant’s performance against industry benchmarks and utilize the insights gained to further improve reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety.
Continuous Improvement: Foster a culture of continuous improvement by utilizing feedback loops, lessons learned, and feedback from operators and maintenance personnel. Regularly update and refine your maintenance strategies and procedures based on the evolving OREDA data and industry best practices.
Remember, the application of OREDA studies and analysis is an iterative process. Regularly review and update your practices based on new data and insights to ensure continuous improvement in the reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety of centrifugal compressors in your existing plant.

