OREDA STUDIES - SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
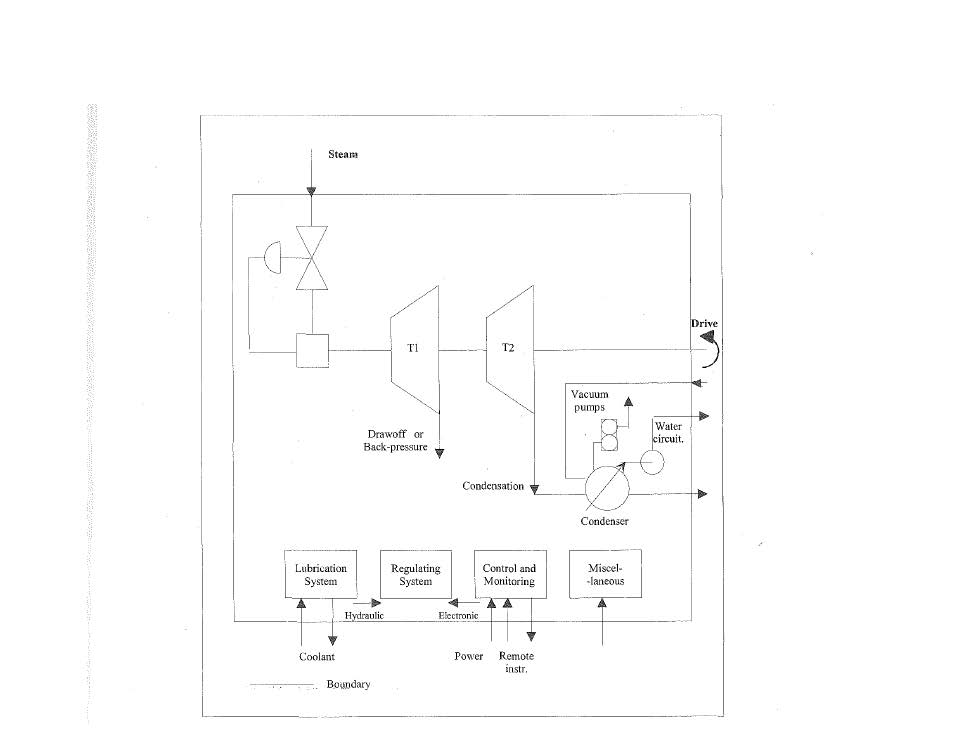
PROCEDURES, ACTIONS, STUDIES, MITIGATION, RECOMMENDATIONS FOR SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
CRITICAL RISKS & FAILURES EVALUATED FOR SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
The OREDA studies also cover special steam turbines, and the procedures, actions, studies, mitigation, conclusions, and recommendations for improving the reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety in these machines are similar to those for centrifugal compressors and gas turbines.
The OREDA handbooks provide failure rate data for various components in steam turbines, including the rotor, bearings, and seals. The failure modes evaluated include bearing failures, blade and vane failures, and damage to the rotor and casings.
To mitigate these failures, OREDA recommends regular inspections and maintenance, including monitoring of vibration and temperature, lubrication checks, and visual inspections of components.
Conclusions drawn from OREDA studies for steam turbines include the importance of proper maintenance and monitoring of critical components, as well as the benefits of using high-quality materials and design features to minimize the risk of failures.
Recommendations for improving reliability and safety include implementing advanced monitoring technologies and predictive maintenance strategies, improving training and awareness of maintenance personnel, and improving design features such as improved blade materials and better lubrication systems.
The OREDA studies also include special steam turbines, such as those used in power generation and other industrial applications. Some of the critical risks and failures that are evaluated include:
Rotor blade failure: This is a critical failure that can lead to catastrophic damage and downtime. The OREDA studies evaluate the probability of this failure mode and recommend mitigation strategies, such as blade inspection and replacement.
Bearing failure: Bearings are critical components in steam turbines, and their failure can lead to significant downtime and repair costs. The OREDA studies evaluate the probability of bearing failure and recommend mitigation strategies, such as lubrication and monitoring.
Seal failure: Steam turbines use seals to prevent steam leaks and maintain efficiency. Seal failure can lead to steam leaks and reduced efficiency. The OREDA studies evaluate the probability of seal failure and recommend mitigation strategies, such as regular maintenance and replacement.
Corrosion and erosion: Corrosion and erosion can lead to degradation and reduced efficiency in steam turbines. The OREDA studies evaluate the probability of corrosion and erosion and recommend mitigation strategies, such as monitoring and protective coatings.
The procedures, actions, studies, mitigation, conclusions, and recommendations obtained in the OREDA studies for special steam turbines are similar to those for other types of machinery. The studies include the collection and analysis of data, evaluation of failure modes, identification of critical risks, and development of mitigation strategies. The OREDA studies provide valuable information for improving the reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety of special steam turbines in oil, gas, and petrochemical industries.
WHY, WHEN, WHERE, WHAT, WHICH, HOW TO APPLY THE OREDA STUDIES & ANALYSIS FOR SPECIAL STEAM TURBINES
Why apply OREDA studies and analysis for special steam turbines?
- OREDA studies provide valuable insights into the performance, failure modes, and maintenance practices related to special steam turbines. By applying OREDA data and analysis, you can gain a better understanding of the reliability issues and failure patterns specific to these turbines. This knowledge enables you to make informed decisions regarding maintenance strategies, equipment design, and operational practices, ultimately improving reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety.
When should OREDA studies and analysis be applied?
- OREDA studies and analysis can be applied at various stages, including during the design phase, equipment procurement, installation, and throughout the operational lifecycle. For existing plants, it is beneficial to conduct periodic assessments using OREDA studies to identify areas for improvement and optimize maintenance practices. For new projects in power generation, OREDA studies can be applied during the design and equipment selection process to ensure reliability and optimize maintenance strategies from the outset.
Where should OREDA studies and analysis be applied?
- OREDA studies and analysis can be applied in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries, both in existing plants and for new projects in power generation. Special steam turbines are commonly used in various applications, including power plants, refineries, and petrochemical facilities. OREDA data and analysis are particularly relevant in these installations to enhance the reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety of special steam turbines.
What can be achieved by applying OREDA studies and analysis?
- By applying OREDA studies and analysis for special steam turbines, you can achieve several benefits:
- Improved reliability: OREDA data helps identify common failure modes, failure rates, and root causes, allowing you to implement proactive maintenance strategies and design improvements to mitigate those issues.
- Enhanced maintainability: OREDA studies provide information on maintenance activities, intervals, and durations, enabling you to optimize maintenance schedules, spare parts management, and procedures to minimize downtime.
- Increased availability: By addressing reliability and maintainability issues, you can reduce unplanned downtime, leading to increased availability and improved power generation efficiency.
- Enhanced safety: OREDA studies can help identify safety-critical components, failure modes, and associated risks. This information can guide the implementation of appropriate safeguards, risk mitigation measures, and safety protocols.
- By applying OREDA studies and analysis for special steam turbines, you can achieve several benefits:
Which specific aspects of OREDA studies should be considered for special steam turbines?
- When applying OREDA studies to special steam turbines, consider the following aspects:
- Failure data analysis: Analyze failure rates, failure modes, and causes specific to special steam turbines. This information can guide reliability improvement efforts.
- Maintenance data analysis: Assess maintenance activities, intervals, and durations to optimize maintenance practices and reduce downtime.
- Common cause analysis: Identify common causes of failures and implement measures to address those issues systematically.
- Risk assessment: Evaluate safety-critical components, potential hazards, and associated risks. Use this information to implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies.
- Benchmarking: Compare your plant’s performance against industry data to identify performance gaps and target areas for improvement.
- When applying OREDA studies to special steam turbines, consider the following aspects:
How to apply OREDA studies and analysis for special steam turbines?
- To apply OREDA studies and analysis for special steam turbines, follow these steps:
Access OREDA Data: Obtain access to the OREDA database or relevant publications specific to special steam turbines. This will provide you with valuable industry data on the reliability, failure modes, maintenance practices, and performance of these turbines.
Collect Plant-Specific Data: Gather relevant data specific to your existing plant’s special steam turbines or the turbines planned for a new project. This includes historical maintenance records, failure data, operational parameters, performance data, and design specifications.
Analyze Failure Data: Analyze the failure data collected from your plant or available in the OREDA database to identify common failure modes specific to special steam turbines. Compare the failure rates and failure modes with industry benchmarks to determine if your plant experiences similar failure patterns.
Root Cause Analysis: Perform a thorough root cause analysis for identified failure modes. Investigate the underlying causes of failures, such as design issues, material degradation, operating conditions, or maintenance practices. This analysis helps you understand the factors contributing to reliability issues and guides improvement efforts.
Review Maintenance Practices: Evaluate your plant’s or project’s current maintenance practices and procedures for special steam turbines. Compare them with industry best practices and recommendations derived from the OREDA data. Identify any gaps or areas for improvement.
Optimize Maintenance Strategies: Based on the findings from the OREDA data and your plant-specific analysis, develop and implement optimized maintenance strategies for special steam turbines. Determine appropriate maintenance intervals, tasks, and procedures. Consider implementing condition-based or predictive maintenance techniques to maximize reliability and minimize downtime.
Spare Parts Management: Assess your spare parts inventory management for special steam turbines. Utilize the OREDA data and industry insights to optimize your spare parts strategy, ensuring that critical components are readily available when needed. Consider establishing strategic partnerships with suppliers to ensure timely availability of spare parts.
Implement Safety Measures: Utilize the OREDA data to identify safety-critical components, failure modes, and associated risks specific to special steam turbines. Evaluate your plant’s or project’s existing safety measures and compare them with industry recommendations. Implement appropriate safeguards, risk mitigation measures, and safety protocols to enhance safety.
Design Optimization (for New Projects): If you’re working on a new project in power generation, leverage the OREDA data and analysis during the design phase. Incorporate lessons learned from OREDA studies into the special steam turbine design to enhance reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety. Consider factors such as component selection, redundancy, accessibility for maintenance, and system integration.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Establish a system for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of your special steam turbine performance. Continuously collect and analyze data on failures, maintenance activities, equipment condition, and performance parameters. Compare your plant’s or project’s performance against industry benchmarks and utilize the insights gained to further improve reliability, maintainability, availability, and safety.
Continuous Improvement: Foster a culture of continuous improvement by utilizing feedback loops, lessons learned, and feedback from operators, maintenance personnel, and other stakeholders. Regularly update and refine your maintenance strategies, procedures, and design practices based on the evolving OREDA data, industry best practices, and technological advancements.